Over the past few years, “smart objects” have become more and more common and their number keeps growing. This offers many opportunities and possibilities in regard to technological innovation, such as automation. These smart objects have the ability to interconnect, which is done through IoT (Internet of Things) protocols. In order to explore these technologies, we have established a wireless IoT network.
LoRaWAN, an advantageous protocol
Within the scope of our operation, we were interested in a particularly eye-catching IoT protocol, the LoRaWAN (long range wide area network) protocol. We chose this technology because it enables the creation of a private network through unlicensed frequency bands. Moreover, this protocol has a standard open to the public, therefore, it is no longer necessary to subscribe to an operator to maintain connections.
In order to test the LoRaWAN network, we first determined as a team the use case to be implemented, the objective being to focus on rapid development and prototyping. Thus, a smart monitoring solution was implemented in our Trialog facilities.
The implementation of a monitoring system
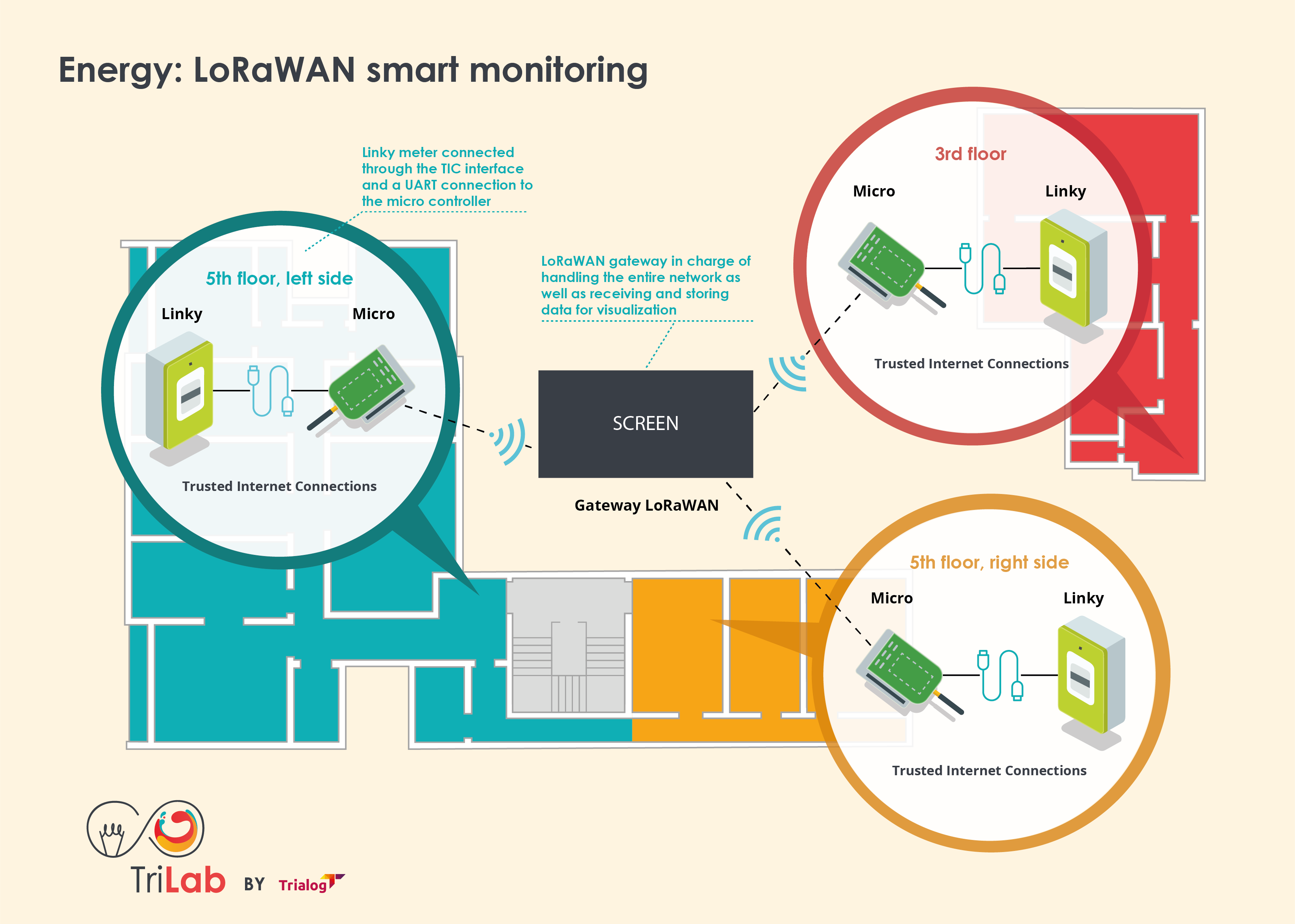
We then deployed a system consisting of Linky meters and customized smart devices in the offices. The purpose of this system is to monitor the electricity consumption of the facilities. Through this system, we can determine which processes are the most consuming and thus reducing the ecological and monetary impact of Trialog’s offices, by finding more ecological alternatives.
In order to have a real monitoring, the possibilities and functionalities of the network and of the system have been evaluated at each stage of the development. During this project, an Open Source version of LoRaWAN was used, and Open Source data storage and visualization software was used to minimize the cost of this prototype. Therefore, we were able to gain experience in network development in their entirety with a visual application.
The choice of these softwares also allowed more flexibility in the development of the smart monitoring system’s functions.
The stakes
This network has three stakes for Trialog :
- The exploration of an IoT wireless technology
Through the state of the art, then the implementation, we were able to learn about the different IoT technologies, and more particularly about their value for smart monitoring.
- Exploring the functions of a smart monitoring system
The design and implementation was an opportunity for us to study the functions of a smart monitoring system, and their applications.
- Improving Trialog’s carbon footprint.
Real-time observation of power consumption at Trialog will allow the CSR team to act on our most energy-demanding usages.
To learn more about LoRaWAn check out our article dedicated to it.